Blog
Learning Materials
Normal Hairline for Men: What It Looks Like
Updated: May 27, 2025

Men's hairlines are not just a trivial aspect of appearance; they reflect a complex interplay of genetics and aging. Studies show that two primary shapes, linear and M-shaped, account for 88.5% of all male hairlines. But here’s the surprising part: the shape isn't what we should be worried about. Many believe a receding hairline is a guaranteed sign of male pattern baldness. However, understanding your hairline's natural progression can be the key to recognizing when something is actually going wrong. With insights into normal hair growth patterns, men can proactively address hair health rather than simply accept changes as inevitable.
Table of Contents
- Identifying Common Hairline Shapes For Men
- Gauging Changes In Your Hairline
- Understanding Hairline Types And Aging
- Factors Affecting Your Hairline Shape
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Understanding Hairline Morphologies | Men's hairlines typically fall into linear or M-shaped categories, which are the most common shapes observed. |
| Stages of Hairline Progression | Hairlines evolve through defined stages: juvenile, middle, and receding, with each stage reflecting natural maturation and hormonal influences. |
| Factors Influencing Hairlines | Genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental factors significantly determine hairline shape, recession patterns, and potential balding tendencies. |
| Recognizing Hair Loss Indicators | Key indicators of concerning hairline changes include rapid recession, thinning at temples, and significant scalp visibility during normal lighting. |
| Professional Assessment is Crucial | Regular monitoring and professional consultation with dermatologists can help identify changes and guide interventions for healthy hair maintenance. |
Identifying common hairline shapes for men
Understanding the variations in male hairlines is crucial for recognizing normal hair growth patterns and potential changes over time. Men's hairlines are not uniform, with several distinct shapes and characteristics that develop naturally throughout their lifetime.
Natural Hairline Morphologies
Research reveals that men's hairlines typically fall into specific morphological categories. A comprehensive Japanese study found that two primary frontal hairline shapes dominate among male populations: linear and M-shaped hairlines, which collectively represent 88.5% of observed patterns.
The linear hairline appears relatively straight across the forehead, creating a more uniform horizontal boundary between facial skin and hair-bearing scalp. In contrast, the M-shaped hairline features subtle recession at the temples, forming a gentle, asymmetrical curve that resembles the letter M. This shape is particularly common as men transition from juvenile to mature hairline stages.
Hairline Progression and Maturation
A man's hairline is not static but evolves through different stages. Research from hair restoration experts indicates that the mature male hairline typically develops a convex shape, with the highest point of curvature located strategically on the forehead. This natural progression reflects fundamental genetic and hormonal influences.
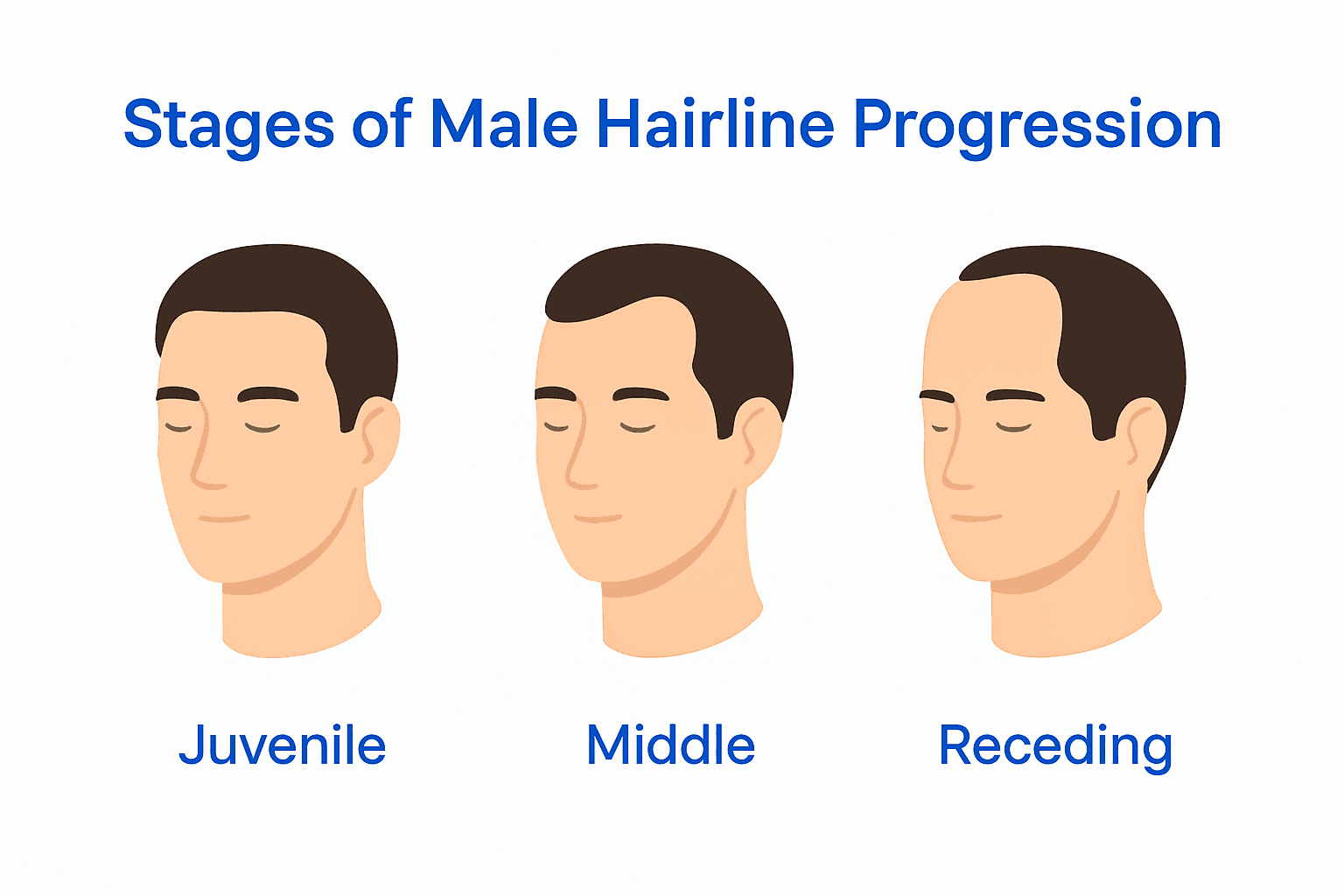
The typical male hairline progression includes three primary stages:
- Low/Juvenile Hairline: Characterized by a lower, more rounded configuration common in younger men
- Middle/Average Hairline: A balanced, symmetrical hairline representing the transitional adult stage
- Receding Hairline: Often forming a more pronounced M-shape as hair density changes with age
Factors Influencing Hairline Characteristics
Medical research from Healthline highlights that hairline shapes are determined by multiple interconnected factors. Genetics play the most significant role, with hereditary traits substantially influencing hairline configuration, recession patterns, and potential balding tendencies.
Hormonal changes, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, significantly impact hairline development. As men age, hormonal shifts can trigger hair follicle miniaturization, leading to gradual changes in hairline shape and density. Testosterone-related genetic sensitivity determines how dramatically these changes manifest.
Environmental factors and lifestyle choices also contribute to hairline characteristics. Stress, nutrition, hair care practices, and overall health can subtly influence hair growth patterns and potentially accelerate or mitigate natural hairline transformations.
While variations exist, understanding these common hairline shapes helps men recognize normal hair development and identify potential early signs of significant hair loss. Consulting with dermatologists or trichology specialists can provide personalized insights into individual hairline patterns and potential interventions.
Gauging changes in your hairline
Monitoring changes in your hairline requires careful observation and understanding of normal hair growth patterns. Men experience unique hairline transformations throughout their lifetime, making it essential to distinguish between normal maturation and potential hair loss indicators.

Identifying Normal Hairline Progression
Research from hair restoration specialists has documented three primary hairline developmental stages: the juvenile hairline, intermediate hairline, and mature male hairline. The juvenile hairline appears concave and sits at the highest forehead crease, while the mature hairline develops a more convex shape positioned slightly higher above the lateral orbital rim.
Normal hairline changes typically occur during early adulthood, with most men experiencing a natural recession between ages 17 and 29. This process, known as hairline maturation, involves a gradual upward movement of approximately 1-2 centimeters. The transformation is generally symmetrical and occurs gradually, without significant hair density loss.
Recognizing Potential Hair Loss Indicators
Clinical studies reveal significant variations in hair density across different scalp regions. The parietal site maintains the highest density at 138.6 hairs per square centimeter, while the temporal region shows lower density at 73.7 hairs per square centimeter. Understanding these baseline measurements helps men distinguish between normal hairline changes and potential hair loss.
Key indicators of concerning hairline changes include:
- Rapid or asymmetrical recession beyond 2 centimeters
- Significant thinning at temple regions
- Visible scalp exposure during normal lighting
- Increased hair shedding during grooming
- Formation of distinct balding patterns
Professional Assessment and Monitoring
Specialized research highlights that male hairlines naturally exhibit subtle asymmetries, with a predominant rightward skew. This finding underscores the importance of professional evaluation when assessing potential hair loss.
Dermatologists and trichology experts recommend several monitoring strategies:
- Photograph your hairline quarterly from consistent angles
- Track hair density using digital imaging technologies
- Document any changes in hair texture or scalp condition
- Maintain a detailed personal and family hair loss history
Advanced diagnostic techniques like scalp microphotography and trichoscopy can provide precise measurements of hair follicle changes. These methods enable early detection of potential hair loss patterns, allowing for proactive intervention strategies.
While hairline changes are normal, persistent or dramatic transformations warrant professional consultation. Understanding your unique hair growth patterns empowers you to make informed decisions about potential treatments or lifestyle modifications that support healthy hair maintenance.
Understanding hairline types and aging
Hairline characteristics evolve significantly throughout a man's life, reflecting complex interactions between genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and aging processes. Understanding these transformations helps men recognize normal hair development and potential genetic patterns.
Classification Of Hairline Morphologies
Research from Japanese studies provides fascinating insights into male hairline diversity. The research categorized male hairlines into four primary types:
- Linear Hairline: Straight and uniform, found in 45.9% of men
- M-shaped Hairline: Deep fronto-temporal recession, observed in 42.6% of subjects
- Round Hairline: Softly curved configuration, representing 10.7% of men
- Triangular Hairline: Rare configuration, accounting for only 0.82% of the population
Progression Of Hairline Changes
The Hamilton classification system offers a comprehensive framework for understanding male pattern baldness progression. This systematic approach identifies eight distinct stages of hairline transformation, ranging from minimal recession to extensive hair loss:
- Type III represents borderline cases with initial recession
- Type IV demonstrates minimal baldness with deep frontotemporal areas
- Types V-VIII showcase progressive hair loss patterns
Interestingly, the Basic and Specific (BASP) classification system indicates that younger and older males typically maintain minimal frontal hairline recession, classified as type M1;2.
Factors Influencing Hairline Aging
Multiple physiological factors contribute to hairline changes as men age:
- Hormonal Shifts: Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels significantly impact hair follicle behavior
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited traits determine hairline characteristics and potential recession patterns
- Metabolic Changes: Alterations in cellular metabolism affect hair follicle health and regeneration
Genetic factors play a predominant role in determining individual hairline trajectories. Some men experience minimal changes, while others might encounter more pronounced recession. The rate and pattern of hairline transformation vary widely among individuals, making personalized assessment crucial.
Environmental factors such as stress, nutrition, and overall health also subtly influence hairline development. Chronic stress, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions can accelerate or modify natural hairline progression.
Understanding these nuanced changes empowers men to make informed decisions about hair care, potential interventions, and realistic expectations regarding their hairline's natural evolution. Professional consultation with dermatologists or trichology specialists can provide personalized insights into individual hairline characteristics and potential management strategies.
Factors affecting your hairline shape
A man's hairline is a complex biological feature influenced by multiple interconnected factors. Understanding these diverse elements helps individuals comprehend the unique characteristics of their hair growth patterns and potential future changes.
Genetic Determinants
Research from specialized dermatological studies reveals that genetics play the most critical role in determining hairline shape. Multiple genes interact to define the precise location, configuration, and potential recession patterns of an individual's hairline. Genetic inheritance is typically unpredictable, meaning that a man's hairline might not exactly mirror his parents' patterns.
Family history provides crucial insights into potential hairline development. Men with close relatives experiencing early hairline recession or specific baldness patterns are more likely to experience similar transformations. The genetic blueprint includes information about hair follicle sensitivity to hormones, hair density, and potential susceptibility to pattern baldness.
Ethnic and Racial Variations
Comprehensive studies on global populations demonstrate significant differences in hairline characteristics across racial groups. These variations highlight the intricate relationship between genetic heritage and hair growth patterns:
- Caucasian Men: Typically develop a V-shaped mature hairline with more pronounced temple recession
- African American Men: Often exhibit broader, flatter hairline configurations with less dramatic recession
- Asian Men: Tend to have wider, more uniform hairline distributions with gradual changes
These ethnic variations reflect complex genetic adaptations and evolutionary traits specific to different population groups. The width, density, and migration pattern of hair follicles vary substantially across racial backgrounds, creating unique hairline characteristics.
Environmental And Physiological Influences
Beyond genetic factors, multiple environmental and physiological elements significantly impact hairline shape and development. Hormonal changes, particularly testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, dramatically influence hair follicle behavior and potential recession.
Key physiological factors include:
- Hormonal fluctuations during puberty and early adulthood
- Metabolic health and nutritional status
- Stress levels and psychological well-being
- Overall endocrine system functioning
External environmental factors also play a nuanced role. Prolonged exposure to environmental stressors like pollution, extreme temperatures, and UV radiation can subtly impact hair follicle health. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in proteins, vitamins, and minerals essential for hair growth, can accelerate potential hairline changes.
Chronic medical conditions, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications can also influence hairline characteristics. Conditions like thyroid disorders, scalp infections, and treatments such as chemotherapy can temporarily or permanently alter hair growth patterns.
Understanding these multifaceted influences empowers men to adopt proactive approaches to hair health. While some factors remain beyond individual control, maintaining overall health, managing stress, and consulting healthcare professionals can help optimize hair growth potential and manage potential hairline transformations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered a normal hairline for men?
A normal hairline for men typically falls into linear or M-shaped categories, which reflect common shapes observed in male populations.
How does a hairline progress as men age?
Men's hairlines evolve through defined stages: juvenile, middle, and receding. These stages indicate natural maturation and hormonal influences as men age.
What are the signs of potential hair loss in men?
Key signs of potential hair loss include rapid recession beyond 2 centimeters, significant thinning at the temples, visible scalp exposure in regular lighting, and noticeable hair shedding during grooming.
How can I monitor changes in my hairline?
To monitor changes, consider photographing your hairline quarterly, tracking hair density using digital imaging, and documenting any changes in hair texture or scalp condition.
Discover Your Unique Hairline Journey with MyHair.ai
As you navigate the complexities of normal hairline progression, understanding your individual patterns becomes paramount. Rapid recession, thinning at the temples, and changing hair density are common concerns for many men facing hair loss. At MyHair.ai, we leverage cutting-edge AI technology to provide you with personalized insights into your hair health. Our advanced algorithms analyze your specific hair issues, helping you differentiate between normal maturation and potential problems.

Don’t leave your hair’s future to chance! Start tracking your hair changes today and receive tailored product recommendations designed specifically for your needs. Take the first step towards restoring your confidence—visit https://myhair.ai now to upload your scan and unlock custom insights. Your hair deserves the best, and with MyHair.ai, you’re just a click away from understanding and improving your hair health!